Purpose: To share news about innovative information systems to support environmental sustainability.
About Me

- M. A. Achachlouei
- Lund, Skåne, Sweden
- Student at Lund University, IT Systems Analyst & Designer
Wednesday, December 8, 2010
IT for Sustainability: Capgemini's Approach
Thursday, November 18, 2010
Internet of Things for a Green Planet: 2010 Conference
Wednesday, November 17, 2010
ICT for Sustainable Growth - European Commission
Tuesday, November 16, 2010
Commercialization of sustainable energy technologies
Monday, November 15, 2010
The Impact of Climate Change on M&A Activity
- Climate change is now a mainstream issue and making a real impact on mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity.
- Climate change is fast becoming a board agenda item for successful acquirers.
- Link: http://www.siliconrepublic.com/download/fs/doc/reports/drivingchangeclimatesurvey.pdf
- Analysts estimate that 2007 saw US$55.7bn in M&A transactions – up by 47pc on the year before.
- This report was written in co-operation with the Economist Intelligence Unit and is based on a survey of 202 senior executives from across the global energy industry, conducted in February 2008.
- Link: http://www.siliconrepublic.com/download/fs/doc/reports/turninguptheheat.pdf
Sunday, November 14, 2010
Sustainable Economy Based on Prosperity
International Organizations to Promote Sustainability
- The Brundtland Commission (formally the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED))
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brundtland_Commission - Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
http://www.ipcc.ch/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intergovernmental_Panel_on_Climate_Change - World Energy Council,
"Founded in 1923, the World Energy Council is the only truly global and inclusive forum for thought-leadership and tangible engagement committed to our sustainable energy future. Our network of 93 national committees represents over 3000 member organizations including governments, industry and expert institutions. Our mission is to promote the sustainable supply and use of energy for the greatest benefit of all. The World Energy Congress is the world's premier energy gathering."
http://www.worldenergy.org/
Saturday, November 13, 2010
GIS for Sustainability
Authors
Abstract:
Tools that support public engagement with sustainability are essential for local sustainability planning. This research investigates the ability of two geographic information system (GIS)-based tools to promote discussion of sustainability in a suburban context. A local ecological footprint tool and a community environmental atlas (an environmentally themed online mapping system) were created for seven suburban boroughs of Montreal. Variations of both tools have been used to support sustainability efforts, but their use has not been widely evaluated. Working from a public participation GIS (PPGIS) framework that recognizes the powerful influence of data representation, this research uses focus groups to evaluate how well these tools address three criteria that have emerged from the literature on public engagement in sustainability: interdependency across systems, reflexivity about personal and social decision making, and interactions across spatial scales. Whereas the atlas remains advantageous for discussing local spatial specifics, it was found that the ecological footprint helped people see the interconnections among systems, integrate local and global aspects of sustainability, and reflect on the values and assumptions underlying current social and economic structures.
Alternative Development: Beyond Ecological Communities and Associations
Alternative Development: Beyond Ecological Communities and Associations
Friday, November 12, 2010
Geographical information systems applied in the field of renewable energy sources
Geographical information systems applied in the field of renewable energy sources
Javier Domínguez and Julio Amador (2007)
http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1231681
Abstract:
This article presents a synthetic vision of geographical information systems (GIS) applications that are state of the art in the renewable energy field. The objective is to analyze the main qualities and problems of these applications, focusing on specific samples, and to carry out a methodological proposal in this genre. From this point of view, the study synthesizes the analyzed applications in three big groups: Decisions Support Systems (DSS) based on GIS; renewable energy and distributed generation of electricity; and decentralized generation for the rural electrification. In addition, a synthetic table and bibliographical references is provided for each group. Finally, several conclusions and a methodological outline are contributed for GIS application in the rural electrification with renewable energy.
Friday, November 5, 2010
European Commission: The future impact of ICT on environmental sustainability
http://fiste.jrc.ec.europa.eu/download/interim_report_1_final.pdf
Thursday, November 4, 2010
Design Research in Information Systems
Vaishnavi and Kuechler have published a web page on Design Research in Information Systems (IS). The page is intended to provide design researchers in information systems as well as others interested in design research with useful information on understanding, conducting, evaluating, and publishing design research.
10 Research Questions: IS innovation for Sustainability
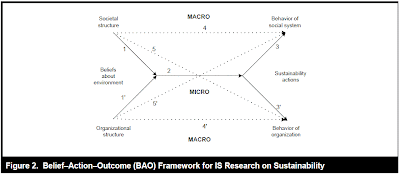
Melville (2010) develops a research agenda (with ten research questions) on information systems innovation for environmental sustainability. This agenda, which is drawn upon a framework called Belief- Action-Outcome, demonstrates "the critical role that IS can play in shaping beliefs about the environment, in enabling and transforming sustainable processes and practices in organizations, and in improving environmental and economic performance."
The following excerpts are selected from this research agenda (Melville 2010):
Given the complexity of the topic, the first two research questions underscore the need for diverse knowledge-creation approaches (positivist, interpretive, critical, and design) and theories in studies of IS for environmental sustainability.
- Research Question 1: How can different philosophical perspectives—positivist, interpretive, critical, and design—be applied to complex problems involving information systems, organizations, and the natural environment?
- Research Question 2: How can different theories be applied to complex problems involving information systems, organizations, and the natural environment?
Two research questions address research methodologies and metrics important to the sustainability domain but relatively new to IS scholarship, including life-cycle analysis, integrated assessment, and system dynamics modeling.
- Research Question 3: How can different research methodologies, such as life cycle analysis and integrated assessment, be applied to examine complex problems involving information systems, organizations, and the natural environment?
- Research Question 4: How can different environmental metrics, such as CO2 equivalent, be employed to assess the impact of IS on the natural environment?
The last set of six research questions addresses substantive issues in each of the three domains of the BAO framework for IS research on sustainability, such as how unique characteristics of the sustainability context (e.g., altruism) shape individual intention to use information systems for sustainability. Taken together, the BAO framework and research questions provide the basis for theory development in the realm of IS for sustainability.
- Research Question 5a: What is the impact of information systems on beliefs about the natural environment and environmental sustainability?
- Research Question 5b: What design approaches are effective for developing information systems that influence human beliefs about the natural environment?
- Research Question 6a: How do the distinctive characteristics of the environmental sustainability context, such as values and altruism, affect intention to use and usage of information systems for environmental sustainability?
- Research Question 6b: What design approaches are effective for developing information systems that influence human actions about the natural environment?
- Research Question 7: What is the association between information systems and organizational and sustainability performance?
- Research Question 8: What is the association between information systems and supply chain performance from an efficiency and environmental perspective?
- Research Question 9: How can firms optimally invest in industry IS platforms intended to reduce negative externalities associated with the natural environment?
- Research Question 10: How can systems approaches shed light on organizational and environmental outcomes that result from the use of IS for environmental sustainability?
Monday, November 1, 2010
HCI Research and Environmental Sustainability
Thursday, October 21, 2010
Sustainability Defined
- Sustainability is a complex term that can encompass environmental, economic, and societal issues.
- In essence, sustainability is conservation, deployment, and reuse of resources in responsible ways—a responsibility that is geared toward the triple bottom line. The triple bottom line—people, planet, and profit—view of value creation balances commercial and societal goals in a way that all three Ps are addressed simultaneously rather than being seen as trade-offs or with one goal overriding the other two.
- An encompassing definition of sustainability is “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”
(WCED 1987, p. 43). - This definition is related to the triple bottom line, a broad conceptualization of organizational performance comprising economic, environmental, and social dimensions (Kleindorfer et al. 2005; Porter and Kramer 2006).
Energy Informatics Framework

Belief–Action–Outcome Model
The Role of IS in Achieving the Three Eco-Goals
- eco-efficiency (DeSimone et al. 1997),
- eco-equity (Gray and Bebbington 2000), and
- eco-effectiveness (McDonough and Braungart 1998).
The Four Dimensions of The Sustainability Portfolio
Three decades into the environmental revolution, many companies in the industrialized nations have recognized that they can reduce pollution and increase profits at the same time. But beyond corporate "greening" lies the enormous challenge--and opportunity--to develop a sustainable global economy, one that the planet is capable of supporting indefinitely. Stuart Hart, director of the Corporate Environmental Management Program at the University of Michigan School of Business, explains the imperative of sustainable development and provides a framework for identifying the business opportunities behind sustainability. The dangers today are clear: exploding population growth, rapid depletion of resources, and ever more industrialization and urbanization are creating a terrible environmental burden. Companies normally frame greening in terms of risk reduction, reengineering, or cost cutting. But, says Hart, when greening becomes part of strategy, opportunities of potentially staggering proportions open up. A number of companies are moving in that direction. BASF, for example, is colocating plants to make the recycling of waste feasible, and Xerox is reusing parts from leased copiers on new machines. Hart identifies three stages of environmental strategy: pollution prevention, product stewardship, and the development of clean technology. But companies will not benefit from such efforts unless they draw a road map that can show them how new products and services must evolve and what competencies they will need. Businesses that create a vision of sustainability will be ready to take advantage of the opportunities presented by the need for a sustainable global economy. INSETS: Aracruz Celulose: A Strategy for the Survival Economy.;The Sustainability Portfolio;Building Sustainable Business Strategies.
Three Categories for Sustainability Issues: Generic, Value Chain, and Competitive Context
Wednesday, October 20, 2010
Research Groups Around The World, Interested in IS for Sustainability
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill:
- Arvind Malhotra
- Nigel P. Melville
- Richard T. Watson
- Adela J. Chen
- Marie-Claude Boudreau
- Elena Karahanna
- Jason Dedrick
- Elizabeth Goodman
- Jacqueline Corbett
- Jane Webstery
- Koray Sayiliz
- Ivana Zelenika
- Joshua Pearce
- Ali Dada
- Elgar Fleisch
- Tim S. McLaren
- Priscilla R. Manatsay
- Ron Babinz
- Mohamad Taha Ijab
- Alemayehu Mollay
- Asmare Emerie Kassahunz
- Say Yen Teoh
- Jan Recker
- Stefan Seidel
- Jan vom Brocke
- Wietske van Osch
- Michel Avital